
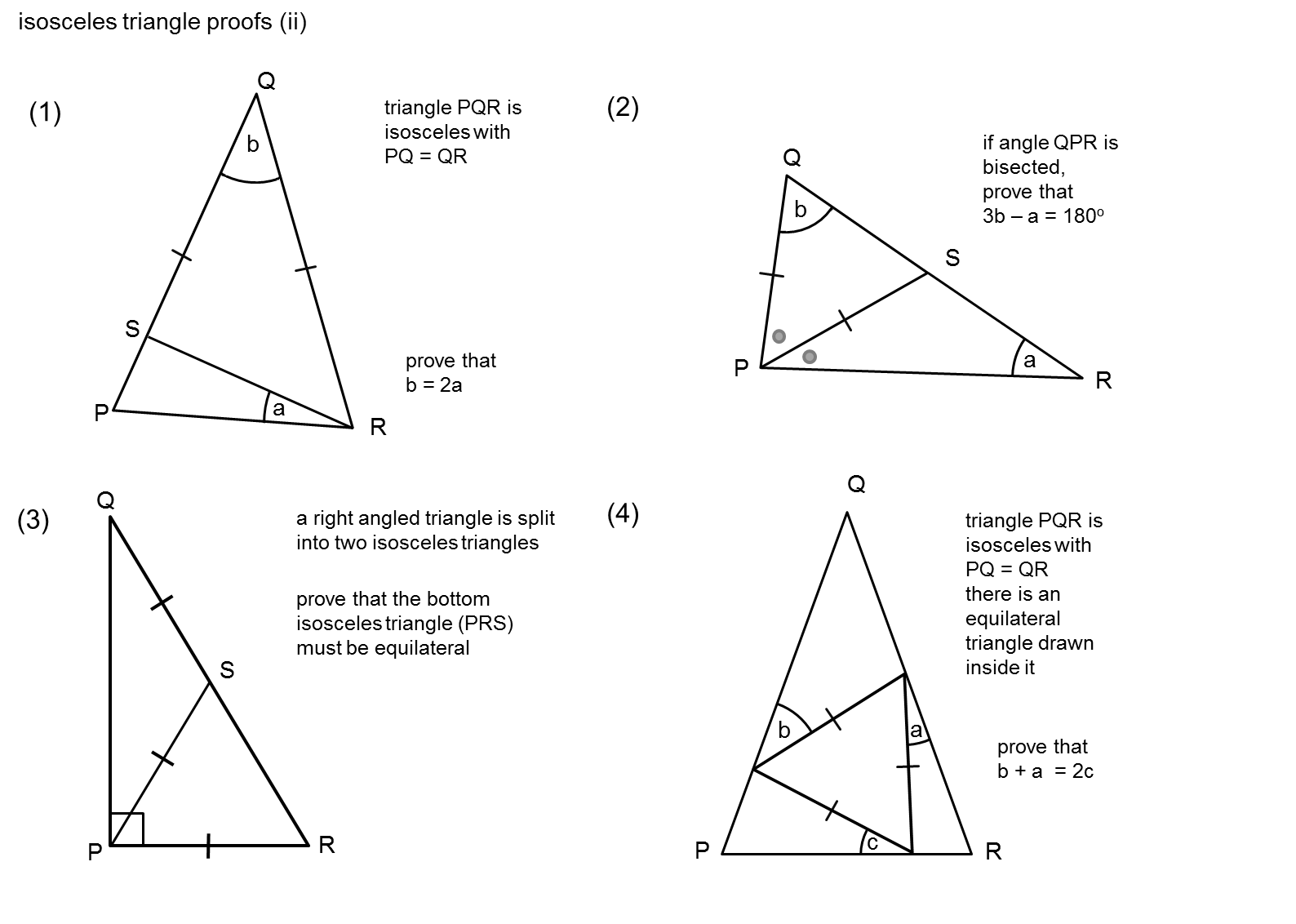
Thus, the perimeter of the isosceles right triangle formula is 2x + l, where x represents the congruent side length and l represents the hypotenuse length. In ∆PQR shown above with side lengths PQ = QR = x units and PR = l units, perimeter of isosceles right triangle formula is given by PQ + QR + PR = x + x + l = (2x + l) units. The perimeter of an isosceles right triangle is defined as the sum of all three sides. Thus, l = x√2 units Perimeter of Isosceles Right Triangle Formula Let's look into the diagram below to understand the isosceles right triangle formula. Isosceles right triangle follows the Pythagoras theorem to give the relationship between the hypotenuse and the equal sides. It is derived using the Pythagoras theorem which you will learn in the section below. So, if the measurement of each of the equal sides is x units, then the length of the hypotenuse of the isosceles right triangle is x√2 units. It is √2 times the length of the equal side of the triangle. The hypotenuse of a right isosceles triangle is the side opposite to the 90-degree angle. If the congruent sides measure x units each, then the hypotenuse or the unequal side of the triangle will measure x√2 units.

Let's look into the image of an isosceles right triangle shown below. The area of an isosceles right triangle follows the general formula of the area of a triangle where the base and height are the two equal sides of the triangle. It is also known as a right-angled isosceles triangle or a right isosceles triangle. It is a special isosceles triangle with one angle being a right angle and the other two angles are congruent as the angles are opposite to the equal sides.
#Right isosceles triangle symmetry full#
If the triangle is rotated a full 360°, it never looks the same except when it arrives back at its original starting position. The order of rotational symmetry of a shape is the number of times it can be rotated around a full circle and still look the same. Rotational symmetryĪ shape has rotational symmetry when it can be rotated and it still looks the same. The number of lines of symmetry in a regular polygon is equal to the number of sides. It has four lines of symmetry and four sides.Ī regular pentagon has 5 sides and 5 lines of symmetry. Only the fourth shape has a line of symmetry Line symmetry in regular polygonsĪ square is a regular polygon. The folded part does not sit perfectly on top of the other part.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
